As many of you probably know, on May 12th, an international cyberattack started infecting more than 230,000 computers in over 150 countries with the worst-hit countries being Russia, Ukraine, India and Taiwan and including many others worldwide. In Europe, some of the worst hit enterprises were Telefonica, FedEx, Deutsche Bahn, Latam Airlines and parts of Britain’s National Health Service.
So how did the WannaCry ransomeware attack occur and how can we prevent it?
Ransomware usually infects a computer with phishing emails, and once any single person in the organization has clicked on it, WannaCry uses the EternalBlue exploit and the DoublePulsar backdoor developed by the U.S. NSA to spread through local networks and remote hosts infecting all systems which do not have the latest security updates installed. Also older Windows systems, such as Windows XP and Windows 2003 are at risk.
Once the WannaCry ransomware is released, it encrypts all data and demands a ransom payment in bitcoins of about 200 to 600 USD.
What tips do we have to prevent the WannaCry ransomware attack or future similar ransomware attacks?
There are some obvious tips, such as never running files you don’t trust… The problem with this is that in big organizations and small alike, you can never have complete control over what people do… Someone is bound to click on that shiny tempting link and download it… but, what you can control is an up-to-date system. If every computer has up-to-date software, then the virus has no say whatsoever in your company.
So how do you ensure that everyone is running the latest versions of their applications and IT components?
1 - Complete your information basis
With consistent standard technology products and up-to-date lifecycles from Technopedia in LeanIX, the basis is set to manage the risk from technology obsolescence. This information is already enough to get started. You might, however, see value in adding additional inputs to estimate the risk of end-of-life technology. LeanIX for example provides the platform to combine all information in one place, be it quantitative or qualitative.
2 - Analyze potential impacts
The simple risk formula states: risk = probability x impact. In the described approach, the main input used for the probability is the lifecycle information provided by the vendor. The next step would be to understand the impacts of technology obsolescence risk and the potential ransomware attack that comes with it. A risk cartography can be used to show relations from IT components (technology layer) via applications (information layer) to business capabilities (business layer). This helps to illustrate complex dependencies and ensure that the risk problem is tackled from a holistic perspective. Looking at the risk cartography, risks can be identified from the infrastructure level and can be traced up to severity of implications for the business.
The severity of the risk can be assessed by many different parameters: How many users are affected by potential ransomware? What revenue impact does a ransomware attack have? What are regulatory or compliance impacts? Does the technology risk result in an inability to meet needs for further business growth?
A good way to further analyze ripple effects in the landscape is to understand how applications are connected. An application that is deeply embedded into the landscape via multiple interfaces can cause severe implications in case of an incident. Imagine a CRM system that is central for customer records and has integrations to Microsoft Exchange, mailing tools, helpdesk tools, content management systems and many more and all this depends on the IT component "Oracle" Due to the high interconnectedness, if Oracle were to be affected by the ransomware, the potential implications on other applications and processes multiply.
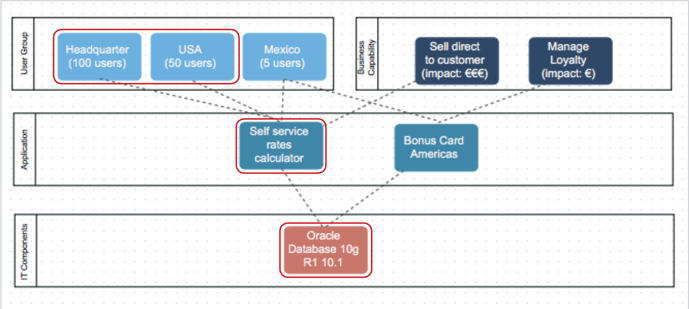
3- Send a simple message
While the risk of obsolete technology probably is intuitively clear to you, it might not be to business leaders. The inputs of your assessment could be many, but in the end the message for leaders needs to be easy to grasp. What should I do? What happens if I don’t do it?
Business capabilities have proven to be a good translation layer between the technical and nontechnical world. Business capabilities encapsulate what a business is doing right now and what it needs to be doing in order to meet current and future challenges. They make life easier, as they are fairly stable over time, are much more tangible than strategy and have the potential to overcome organizational silos. Therefore, they provide the right context to present technology risk.
Have a look at the representation below. It encapsulates the impact of a (potential) WannaCry ransomeware attack from lifecycle to business value in a single report. The colored boxes represent different applications. Applications are supported by underlying technology, such as Windows XP for example. Based on the lifecycle information fed in from Technopedia, we can see which other applications an components can be directly affected:
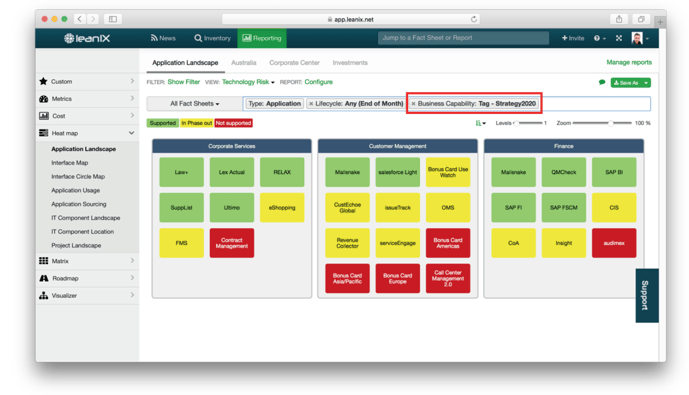
But the report tells much more than the applications affected by technology obsolescence. It links them to Business Capabilities. The report above shows the three Business Capabilities that are marked as being part of the Strategy 2020 program. Especially the Customer Management Capability of the example seems to be affected by risk through outdated technology which could lead to a ransomware attack.
4- Make sure everything is up-to-date
Now that you know where the most critical points lie (those which have the highest business criticality), you should now proceed to (quickly) update the underlying components to their newest version.
We recommend that you start by viewing those applications which have the highest business criticality and view their underlying IT components. These IT components must be updated ASAP. Now that you have the correct prioritization of which IT components and applications must be updated first, you can make sure that the people responsible for updating the systems take care of this.
Next, address the less critical applications, and repeat the process until your IT landscape is 100% WannaCry ransomware safe.
5- Bonus!
Due to the criticality of the WannaCry ransomware attack, we are offering a free expert session on how to avoid this and we will also give you a free LeanIX workspace for a few weeks to try it out! Just book a free session here!
Interested in learning more? Read our Technology Obsolescence whitepaper!


/EN/Reports/Thumbnail-Obsolescence-Gartner.png?width=140&height=100&name=Thumbnail-Obsolescence-Gartner.png)
/EN/White-Paper/EN-IDC-Inforbrief-Application-Rationalization-Portfolio-Management-Thumbnail_v2.png?width=140&height=99&name=EN-IDC-Inforbrief-Application-Rationalization-Portfolio-Management-Thumbnail_v2.png)